diagnostics
– the first step towards effective treatment
– the first step towards effective treatment
Why dental X-ray diagnostics is performed
During the diagnostics and treatment of teeth, not only clinical examination is important, but also the identification and analysis of hidden tooth infection or bone destruction. For this purpose, X-ray diagnostics are carried out, and it allows to quickly obtain necessary information, to establish the diagnosis, assess the dynamics and results of treatment.
What is X-ray diagnostics of the oral cavity?
X-ray diagnostics is a research method that allows you to get pictures of a certain area of the body using X-rays. The device generates them, they pass through the tissues of the body and are perceived by the sensor, forming an image. Bone tissues have the lowest permeability for these rays and are visualized as shadows (although we see them not dark, but light due to the fact that the resulting image is inverted). Modern devices for X-ray diagnostics are digital, which can significantly reduce the radiation load on the patient’s body and speed up the results.
In dentistry, the following types of X-ray examination are distinguished:
- Local (focused) image — method that allows to obtain a 2D-image of 1–4 teeth, assess the condition of bone tissue near the teeth and periodontal tissue in 2D format.
- Orthopantomogram (panoramic dental image) — 2D-image that displays the entire maxillofacial system (unlike the usual X-ray, allows you to simultaneously examine all the teeth), additionally visualized sinuses, temporomandibular joint.
- CT (computed tomography) — 3D-image of the maxillofacial system, which is built from a set of layered virtual “slices” and allows the doctor to explore the entire maxillofacial system or the area of interest from any angle.
When there is a need for X-ray diagnostics?
Indications for a focused image of the teeth:
- Diagnosis of carious lesions of teeth, pulpitis, periodontitis
- Teething problems
- Dental canal treatment: at the planning stage and to assess the results.
Orthopantomogram is carried out when:
- There is a need to investigate the condition and position of all teeth, including the eighth teeth
- Orthodontic treatment is planned
- Planning dental prosthetics
CT (computed tomography) has the highest accuracy and widest possibilities among other types of X-ray diagnostics and is prescribed for such indications:
- Planning operations in the dentoalveolar system
- Preparation for orthodontic treatment
- Preparation for dental implantation, sinus lifting, and surgery
- Assessment of injury consequences
- Identification of developmental anomalies
- Examination for teething disorders
- Preparation for complex tooth extraction
- Diagnosis of tumors in the jaw.
Contraindications and limitations
For X-ray diagnostics in general, there are the following contraindications:
- Bleeding in the mouth
- Mental disorders
- Severe condition of the patient
- Immunodeficiency conditions
- Pregnancy (the procedure is carried out in case of acute need, but it is desirable to refrain from it in the first trimester, optimally up to 5 months of gestation).
In any case, radiographic examination is carried out only if there are medical indications. The slightest irradiation is accompanied by a targeted X-ray of the teeth, and in some cases, it has to be repeated many times during the treatment period. The panoramic image is accompanied by a greater level of radiation exposure, its recommended frequency is up to 3–5 times a month. The level of ionizing radiation in CT is slightly higher, so the doctor can prescribe it no more than 3 times a year, or, if necessary, reduce the examination site.
Preparation for X-ray diagnostics
Before the procedure, you need to remove metal jewelry and accessories in the procedure area. If the patient has removable structures in the oral cavity, they also need to be temporarily removed.
What is the procedure of X-ray?
Before the procedure, the patient wears a protective apron to minimize the effect of rays on the body. Further examination is as follows:
- When creating a focused image, the doctor helps the patient to properly position himself in front of the device. On the signal, you have to hold your breath to make the image accurate.
- The panoramic image takes a little longer, and the source of rays rotates around the jaw. It is necessary to keep the position motionless at this time.
- With computed tomography, the patient has to fix a plastic plate with his teeth and lean his face to the support. The device takes hundreds of pictures – virtual slices, in less than a minute.
Frequent questions about X-ray diagnostics
What can be seen on the X-ray of the tooth?
X-ray examination reveals damage to the tooth, its dislocation, caries, dental deposits, cysts, neoplasms, signs of inflammation, changes in bone tissue.
What is the difference between CT of teeth and panoramic image?
The panoramic image is two-dimensional, it is a flat image of both jaws. As a result of CT, the doctor receives a three-dimensional image, which can be viewed from different sides.
Which is better: X-ray of the tooth or CT?
CT is the most accurate method of studying the entire dentoalveolar system, but in many cases, it is enough to perform a focused image of the teeth. The choice is left to the doctor, who determines the indications for this or that method individually for the patient.
Is computed tomography of teeth safe?
CT is accompanied by radiation, but the use of modern devices, as well as compliance with the recommendations on the frequency of examination, make it possible to diagnose without harm to the patient’s health.
For how long a panoramic picture of teeth is valid?
OPTG results are usually considered valid for 6–12 months, but the term depends on the characteristics of the clinical case.
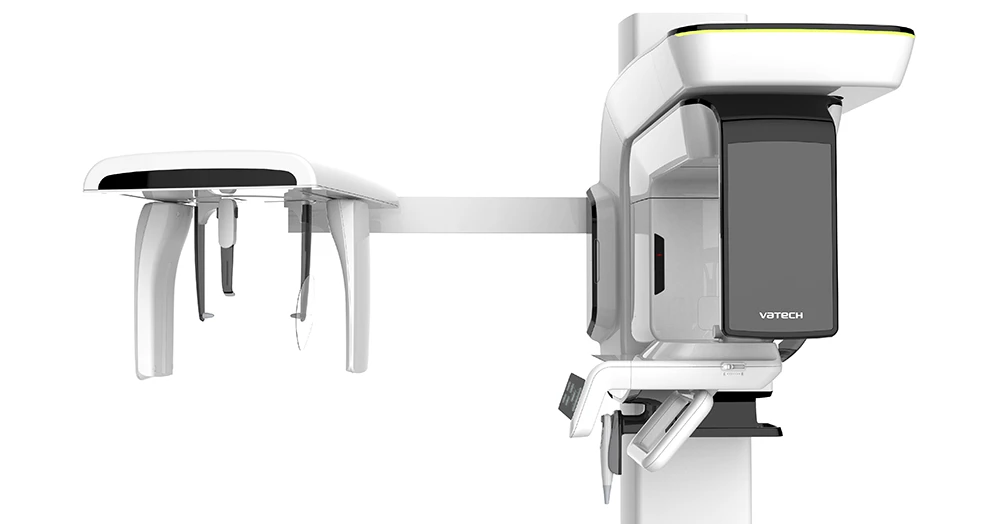
Advantages of our equipment
Our clinic uses a high-quality tomograph Pax-i3D Smart SS (CT + Pano) Vatech with cephalostat, which:
- allows you to get high-resolution images
- works with low radiation exposure – for maximum patient safety
- as a result of one scan allows you to get both a three-dimensional 3D-image and a two-dimensional panoramic image
- minimizes artifacts from metal in the oral cavity, thanks to high-tech image processing.
Cost of basic radiography services
Schedule an appointment with a dentist
