Among dental diseases there are especially dangerous, capable of developing for a long time unnoticed. One common onset of more serious dental problems is periodontitis.
What is periodontitis?
Periodontitis is a gum disease in which there is inflammation in the soft tissues around your teeth. Namely: gum, periodontal ligament, holding tooth in bone, tooth root cement and alveolar sprouts.
Previously, periodontitis was diagnosed in people after 40 years. Today, periodontists note that the prevalence of periodontitis is growing every year, and the age of patients diagnosed with periodontitis has become much younger.
Types of periodontal disease
Depending on the prevalence, there are two types of periodontitis:
- Localized – characterized by inflammation of the gums in the area of 1–2 teeth (most often, this is a mechanical injury to the gums);
- Generalized – characterized by damage to all periodontal tissues (gums, periodontal ligament, destruction of bone tissue).
If you do not undergo timely diagnosis and treatment of periodontal tissues when the first signs of periodontitis are detected, the risk of tooth loss increases significantly.
Causes of periodontitis
The inflammatory process in periodontal tissues can be caused by a number of factors, both general and local.
Local factors include:
- accumulation of bacterial plaque on the surface of tooth enamel
- tartar
- preference for soft foods and dishes in the diet
- irregular and/or improper oral hygiene
- malocclusion
- poor-quality filling, prosthetics, dental implantation or incorrect orthodontic treatment
- incorrect attachment of the bridles of the lips and tongue.
General factors include:
- systemic diseases
- vitamin deficiency (lack of vitamins and minerals)
- hormonal disorders
- smoking
- immunodeficiency
- somatic diseases (blood pathologies, gastrointestinal diseases, diabetes mellitus).
Symptoms of periodontitis
The first symptom of periodontitis is bleeding gums. Subsequently, if you do not consult a periodontist in time, the following complaints and symptoms appear:
- gradual exposure of tooth roots
- mobility of teeth and change in their position in the bone
- bad breath
- dense tartar
- redness and swelling of the gums
- with exacerbation of periodontitis — purulent discharge from periodontal pockets, the formation of abscesses
- discomfort during chewing
- unpleasant sensation similar to itching
- tooth loss.
Diagnosis of periodontitis
To detect inflammation of the periodontal tissues, the following is performed:
- clinical examination of the oral cavity
- radiography
- filling in the periodontal map.
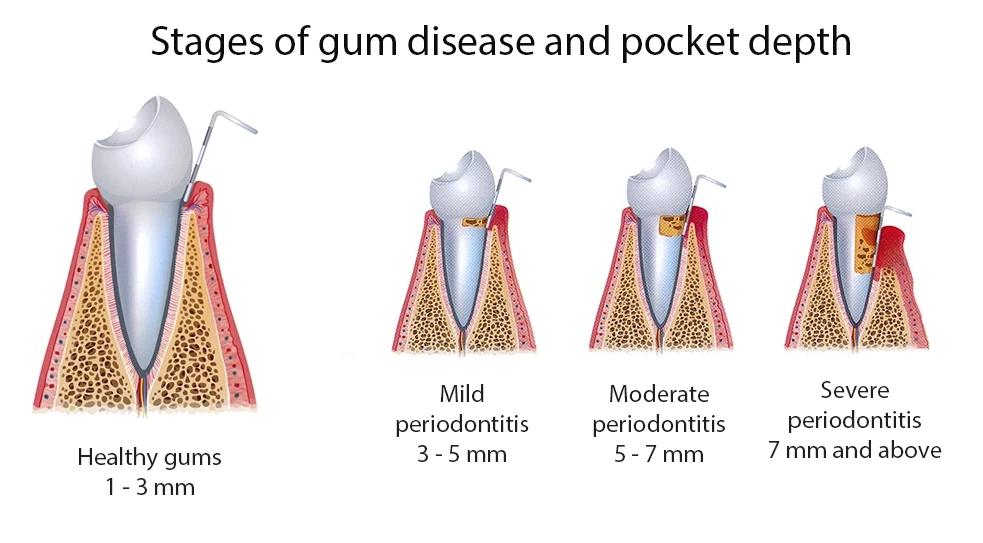
The periodontal map displays information about the state of the gums. With a special periodontal probe, the periodontal doctor diagnoses the presence of a periodontal pocket and measures its depth. The depth of the periodontal pocket helps to assess the degree and course of generalized periodontitis and determine treatment tactics.
Timely diagnosis of periodontal tissue diseases will help keep healthy teeth and gums.
Treatment of periodontitis
In the initial stages of gum inflammation and in the absence of periodontal pockets, it is enough to conduct professional oral hygiene.
It includes:
- indication (staining with a special color indicator) of plaque
- removal of soft, pigmented plaque with special brushes and removal of tartar with special ultrasound nozzles
- polishing the tooth surface with calcium carbonate or glycine granules (AirFlow technology).
The patient is required to conduct a hygiene lesson on which they teach the correct technique of brushing their teeth, select a toothbrush, if necessary, ruffles or a mono-toothbrush, provide recommendations on the choice of toothpaste, floss and determine the individual period of visiting a periodontologist depending on the clinical situation.
In the presence of deep periodontal pockets, curettage is mandatory.
Curettage is a surgical procedure performed by a periodontal physician or dental surgeon with special periodontal, area-specific curettes in order to remove plaque, stone and infected granulation tissue in the periodontal pocket. After high-quality curettage procedure, the tooth root becomes smooth, pathologically altered tissues are eliminated, thereby reducing the depth of the periodontal pocket.
If the patient has one of the causes of periodontitis a common disease, then observation with a family or profile doctor is mandatory.
Prevention of periodontitis
To preserve oral health and reduce the risk of periodontitis, it is advisable to follow the following rules:
- properly and regularly carry out hygienic oral care at home
- regularly carry out preventive examinations at the dentist within the terms recommended by the doctor
- do not miss scheduled visits for professional oral hygiene at the periodontist
- treat chronic diseases in time
- give up smoking or limit the number of cigarettes
- include solid products in the diet at maximum
- follow the rules of good nutrition.
Timely treatment and prevention of periodontitis is a guarantee of health not only of gums and teeth, but also of health in general. The essential thing is to seek help on time.